Electrophoresis
This technique is widely used in laboratories, especially in those of molecular biology, because it is used in important procedures such as: separation, analysis and purification of RNA, DNA, or proteins, nucleic acids, this process is performed because most biomolecules have an electrical charge where their magnitude depends on the pH of the medium in which they are found; because of this, the biomolecules move when subjected to an electric field to the charge pole opposite to that of the molecule.
Its operation is a simple process, separates the molecules according to their size and electrical charge, for this an electric current is used that impels to displace the molecules through a gel or another matrix., then the pores of the gel act as a sieve, allowing the smaller molecules to move faster than the larger molecules, to know the size of the molecules in a sample, they are compared with the established size standards that are separated into the same gel.
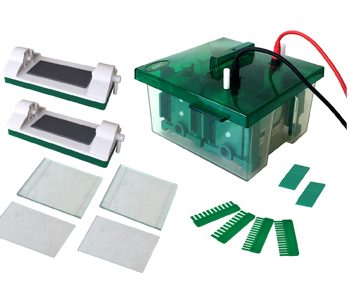
Types of Electrophoresis a Laboratory May Need

Horizontal
In the case of proteins that can have a positive or negative charge, are usually neutral charge, for the migration of molecules pretreatment with detergents, such as sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), which confers negative charge; this homogenizes the proteins in the sample and will all migrate to the positive pole; will only be separated by size.
Now on the side of nucleic acids only have a negative charge, because of their phosphate skeleton, instead electrophoresis, causes nucleic acids to migrate towards the positive pole, called anode. This migration technique is what we call the principle of electrophoresis, where the displacement of the molecules through a gel or other type of porous matrix occurs proportionally, using the parameters of molecular weight or size; movement generated by the electric field.
Vertical
- It has two glass plates of the same thickness and width, but the length varies according to the camera model.
- Two spreaders, which are made of a flexible and resistant material; they determine the thickness of the gel.
- A comb, which is the same thickness as the spreaders and is also made of the same material, polyethylene or Teflon; It is used to mold the aisles where the samples will be placed.
- A support or base: it is a component whose function is to be assembled with the glasses with the spreaders with presses that hold the camera system together.
- The electrophoresis tank: it is the container that contains the run buffer.

In Kalstein you can find the ideal electrophoresis for your Laboratory
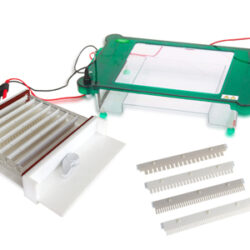
Horizontal Electrophoresis YR03421
YR horizontal gel electrophoresis units have been designed by scientists with the laboratory environment...

Horizontal Electrophoresis YR03422
YR horizontal gel electrophoresis units have been designed by scientists with the laboratory environment ...

Mini-Protean Vertical Electrophoresis Cell
Vertical gel electrophoresis is a more complex set-up compared to horizontal gel system. Researchers normally...
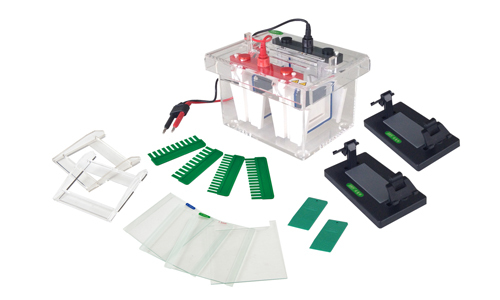
Mini-Protean Vertical Electrophoresis Cell YR03426
Vertical gel electrophoresis is a more complex set-up compared to horizontal gel system. Researchers normally ...
Our Best Selling Electrophoresis
- Intended for protein purification and analysis, ideal for the dimensional electrophoresis, DGGE and preparative gel electrophoresis.
- Equipped with special processing technology aluminums plates, effectively guaranteed the heat dissipation more even, holding stable pH during electrophoresis running.
- Non-proliferation electric field influence, guaranteed the electrophoresis strip more clear and straight. Modular double hinged core cassettes, matched with the basing gel caster, ensuring the whole operation process more convenient.
- Retractable connectors compatible with most major power supplies.
| Model | YR03433 |
| Gel Size(W×L)mm | 120×145 |
| Gel thickness | 1,1.5(mm) |
| Comb wells | 16, 23 |
| Gel capacity | 2 |
| Buffer requirement | 1200(ml) |

Analysis of the best Electrophoresis for your Laboratory

Electrophoresis chamber
The electrophoresis chamber is the device where the sample is introduced for said process; and where the electromagnetic field that is formed in the electrophoresis...

Electrophoresis Applications
Electrophoresis is a laboratory technique in which a controlled electric current is used in order to separate biomolecules according to their size and electric ...

Fundamentals of electrophoresis
Electrophoresis consists of a technique that allows the separation of biomolecules according to their mobility...

What are the principles of electrophoresis?
This technique is widely used in laboratories, especially in those of molecular biology, because it is used...
Electrophoresis models catalog on offer
-
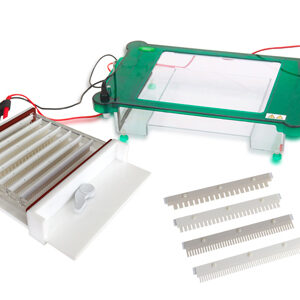
Horizontal Electrophoresis YR03421
-

YR03415 Horizontal Electrophoresis Cell
-

Cellulose Acetate Membrane Horizontal Electrophoresis YR03423
-
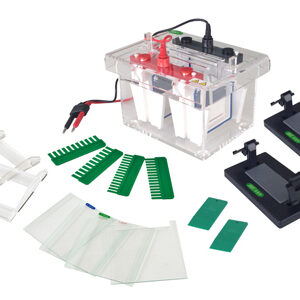
Mini-Protean Vertical Electrophoresis Cell YR03426
-

Horizontal Electrophoresis YR03419
-
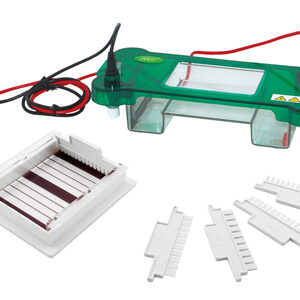
Horizontal Electrophoresis YR03416
-

Vertical Gel Electrophoresis Cell YR03429
-

Horizontal Electrophoresis YR03418
Guides to Becoming an Electrophoresis Expert
Electrophoresis: what are the necessary reagents?
Electrophoresis is an analytical technique in which a controlled electric current is used in order to separate biomolecules...
Electrophoresis: What is it? and What is it used for?
Electrophoresis is one of the main molecular biology techniques, they are considered the most used technique in ...
Advantages of Electrophoresis in Food?
To establish the identity of plant or animal species for food purposes, based only on the observation of external ...
Horizontal and vertical electrophoresis: molecular weight
Gel electrophoresis is a laboratory technique used in genetics to separate mixtures containing DNA, RNA, and other proteins according to their respective molecular size and charge. Gel electrophoresis can be of two different methods: horizontal gel electrophoresis ...

Frequently Asked Questions about Electrophoresis
How to know the prices of Electrophoresis?
To know the price of Electrophoresis we invite you to send us an email with your request through the contact form.
What are the delivery times of the Electrophoresis?
- If the equipment of your interest is in stock or if it must be manufactured.
- The type of freight you have chosen, this may be; air or sea.
How to make a purchase of Electrophoresis?
- By email: [email protected]
- By telephone: +33 (0) 1 78 95 87 02
- E-commerce: Via Kalstein's official website in your country.
How does the warranty work?
Can I request a quote online?
Of course, you can request a quote for the Kalstein team of your interest, directly from our official website. Once you have identified your preferred model, click HERE
